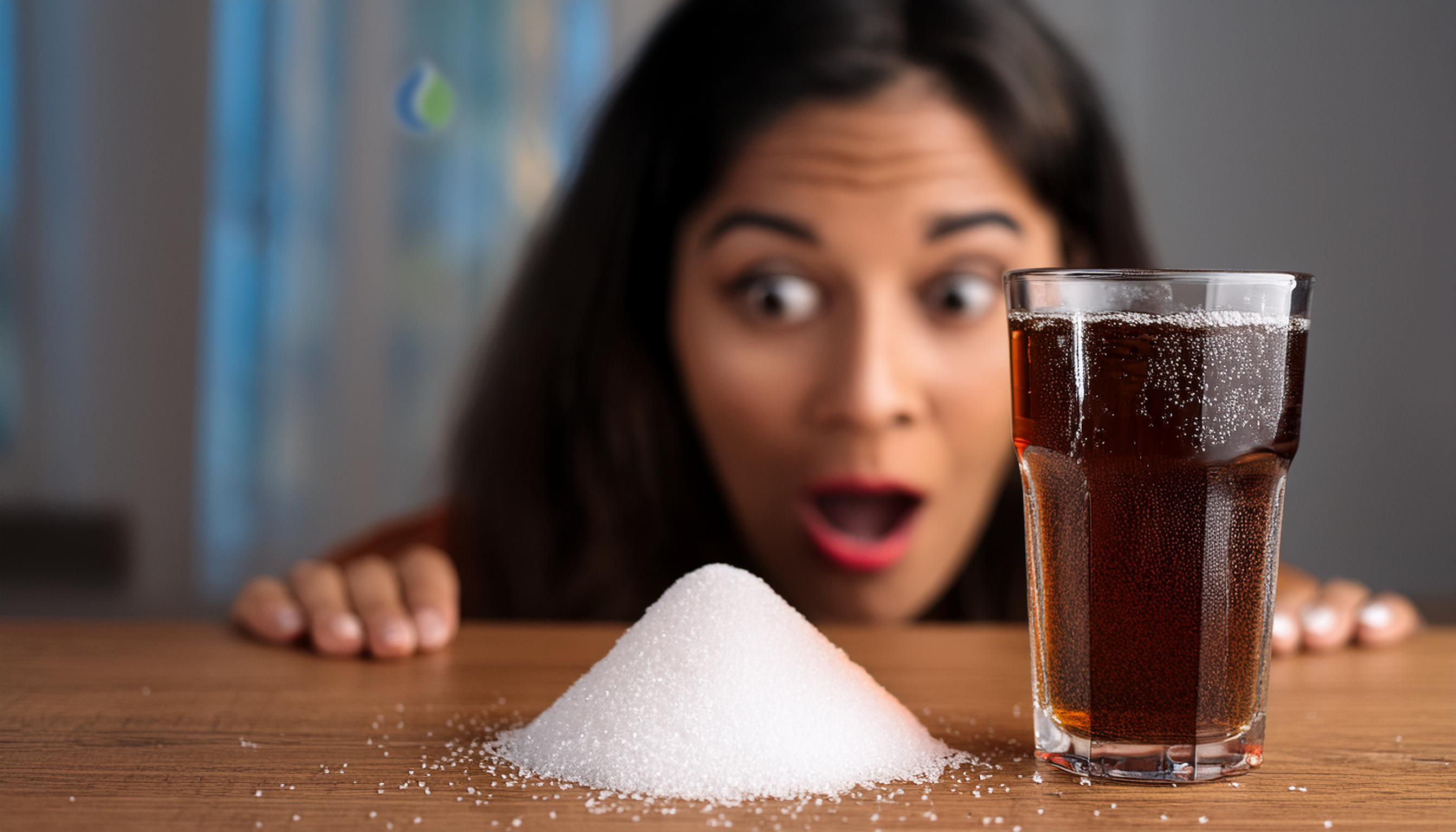
Sugar, an omnipresent ingredient in our modern diet, is often a topic of discussion when it comes to health and well-being. It is found almost everywhere, from our coffee and tea to our snacks and meals. But what exactly does sugar do to our bodies? This extensive blog from Meditech Europe delves deep into the many negative effects of sugar on our health and why it is essential to limit our sugar intake.
What is Sugar?
Sugar is a simple carbohydrate that provides energy to our bodies. The most common forms of sugar are glucose, fructose, and sucrose. While sugar itself is not necessarily bad, the problem becomes apparent when we consume it in large quantities, often without realizing it. Many processed foods contain hidden sugars that contribute to excessive intake.
Demineralization by Sugar
Calcium and Bone Health
Sugar is known to disrupt the mineral balance in our bodies, especially calcium. The process of demineralization involves sugar pulling calcium from our bones, leading to osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is a condition where bones become brittle and weak, significantly increasing the risk of fractures. This is particularly concerning for the elderly and postmenopausal women, who are already at higher risk for bone loss.
Magnesium Deficiency
Magnesium is essential for hundreds of biochemical reactions in our bodies. Excessive sugar consumption can lead to a magnesium deficiency, causing muscle cramps, fatigue, and heart problems. Magnesium also plays a crucial role in regulating blood pressure and the functioning of the nervous system.
Potassium Balance
Potassium is another vital mineral affected by sugar. It is crucial for proper muscle and nerve function. A disrupted potassium balance can lead to muscle weakness and heart rhythm disorders, which can cause severe health issues.
Sugar and the Immune System
High sugar levels in the blood can severely weaken the immune system. Sugar makes white blood cells less effective at fighting infections. Therefore, people who consume a lot of sugar are more susceptible to illnesses and infections. This means that your immune system is less capable of protecting you against viruses, bacteria, and other pathogens.
Sugar and Heart Disease
Increased Blood Pressure and Cholesterol
Sugar is a significant factor in the development of heart disease. It increases blood pressure and levels of bad cholesterol (LDL) in the blood while lowering good cholesterol (HDL). Unused glucose is converted into saturated fat and cholesterol, which accumulate in the arteries. This leads to arteriosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), increased blood pressure, and a higher risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Sugar and Diabetes
Insulin Resistance
The most well-known disease related to sugar is diabetes, particularly type 2 diabetes. This type of diabetes often develops from prolonged exposure to high levels of sugar, leading to insulin resistance. Insulin resistance means that the body no longer responds effectively to insulin, the hormone needed to absorb glucose from the blood. This results in high blood glucose levels, which can cause severe complications such as nerve damage, kidney damage, and heart disease.
Sugar and Joint Inflammation
Sugar causes inflammation in the body, which can lead to arthritis. Inflammation plays a key role in the development of various types of arthritis, including rheumatoid arthritis. Reducing sugar intake can help decrease inflammation and associated pain.
Hormonal Imbalance
Insulin and Leptin
Sugar disrupts the hormone balance in our bodies. It can affect the production of insulin and leptin, two hormones crucial for regulating our metabolism and appetite. Insulin resistance and leptin resistance can lead to overeating and weight gain, which in turn can cause other health problems such as obesity and metabolic syndrome.
Damage to the Pancreas
The pancreas is responsible for producing insulin. Excessive sugar consumption can lead to overloading of the pancreas, eventually resulting in pancreatic dysfunction and diabetes. Chronic overloading of the pancreas can lead to reduced insulin production and ultimately to the development of type 2 diabetes.
Clogging of Arteries
As mentioned earlier, unused glucose in our bodies is converted into saturated fat and cholesterol. These substances can accumulate in the arteries, leading to arteriosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) and increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. This process also leads to increased blood pressure and can cause dangerous blood clots that block blood flow to vital organs.
Sugar and Obesity
Weight Gain and Obesity
One of the most visible effects of sugar is weight gain. Unused sugar is converted into fat in the body. This extra fat is stored in various parts of the body, leading to overweight and obesity, both significant risk factors for various chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
Sugar as Fuel for Diseases
Fuel for Viruses, Bacteria, and Cancer Cells
One of the most alarming aspects of sugar is that it acts as fuel for various diseases. Sugar feeds viruses, bacteria, parasites, fungi, and even cancer cells. This means that high sugar consumption can promote the growth of these harmful organisms in our bodies, leading to an increased risk of infections and diseases.
Sugar and Skin Aging
Wrinkles and Skin Damage
In addition to internal damage, sugar also causes visible damage to our skin. It causes wrinkles through the process of glycation, where sugar binds to proteins in the skin, such as collagen. This makes the skin less elastic and more prone to wrinkles. Indeed, after cigarettes, sugar is the fastest way to accelerate aging.
Sugar and Skin Spots
Freckles and Brown Spots
Do you have freckles or brown spots on your skin? This may be a sign that sugar is damaging your respiratory and reproductive organs. Sugar causes inflammation in every cell of the body, which can lead to various skin problems.
Sugar: A Concentrated, Crystallized Acid
On a chemical level, sugar is essentially a concentrated, crystallized pure acid. This means it is a very acidic substance that can damage tooth enamel, the digestive tract, and other body tissues. This can lead to tooth decay, stomach ulcers, and other health issues.
Sugar: An Addictive and Destructive Food
Sugar is one of the most addictive and destructive foods on the planet. It works on the same brain mechanisms as drugs like cocaine and heroin, explaining why it is so difficult to resist. Many people are unaware of their sugar intake and its addictive effects, leading to a vicious cycle of overconsumption and health problems.
The Sugar Market: A Gigantic Industry
The sugar market is one of the largest markets we know, with millions of people addicted to sugar. Governments find it difficult to regulate this market due to the enormous financial interests. Tax revenues from the sugar market are significant, and attempts to curb this industry could have serious economic consequences.
Conclusion
Sugar has a devastating impact on our bodies, from demineralization to skin aging and fueling diseases. While it is difficult to avoid sugar completely, it is essential to limit intake and be aware of the effects it can have on our health.
At Meditech Europe, we are ready to support you in finding a healthy balance for your body and mind. Our products and services are designed to help you achieve optimal health and well-being. Contact us today for more information.
With this detailed blog, we hope to provide you with insights into the many negative effects of sugar on our health. It is never too late to make changes to your diet and lifestyle for a healthier life. In a subsequent blog, we will discuss sugar substitutes and their impact on health. Stay tuned for more valuable information and tips on health and wellness.