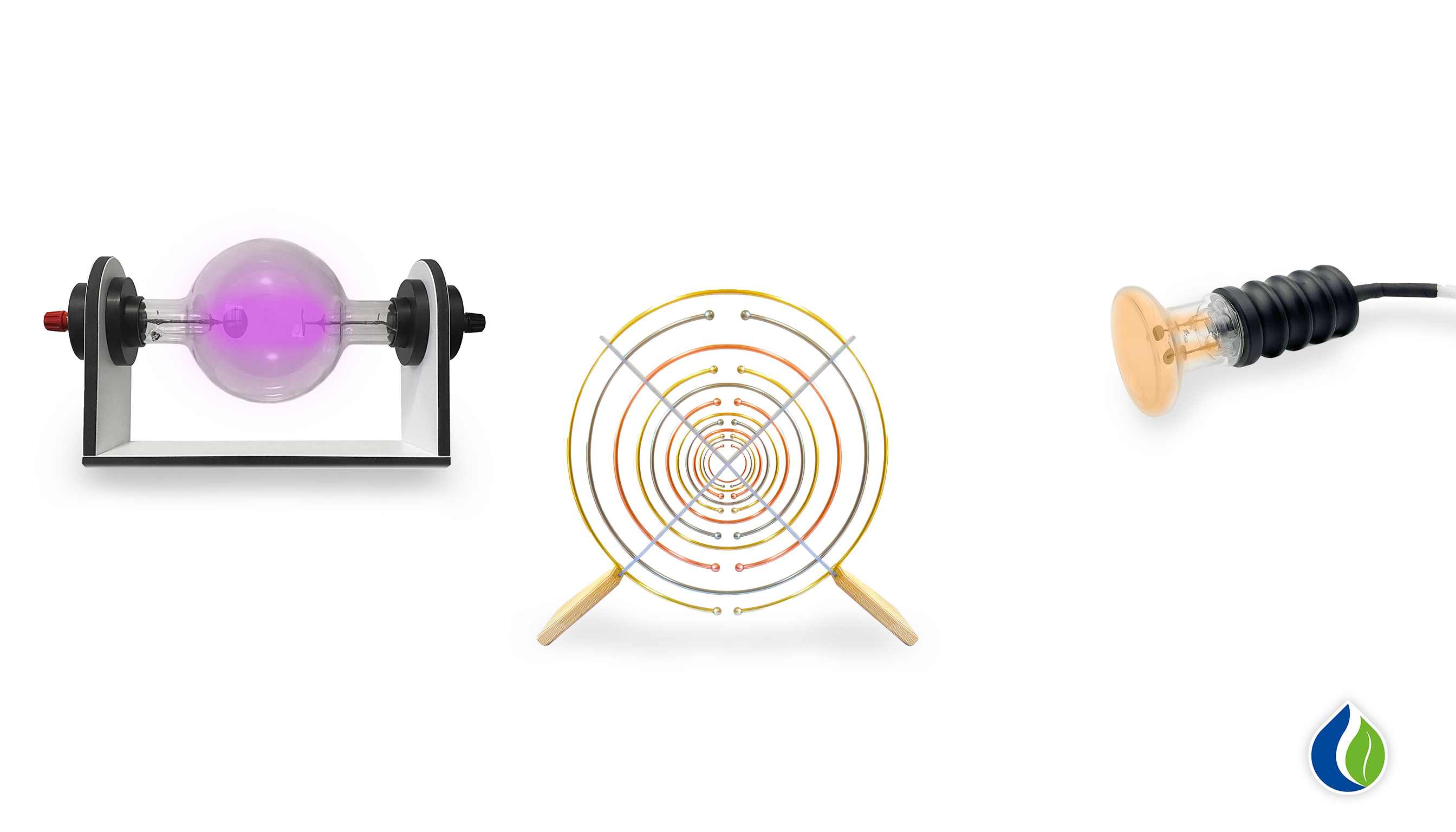
The Multiwave Oscillator (MWO) is a technology renowned for its ability to support biological systems through electromagnetic frequencies. These frequencies can resonate with cellular structures of plants, for example, enabling the overall harmonization and optimization of biological processes. A fascinating aspect of this interaction is the enhancement of biophoton emission – a phenomenon that is crucial for cell health and communication within biological systems.
What Are Biophotons?
Biophotons are ultra-weak light particles emitted by cell structures. They consist of photons, the elementary particles of light, and have an extremely low intensity, often difficult to detect without advanced technology. Biophotons are a natural byproduct of metabolic processes and are closely linked to the functioning of mitochondria, the energy centers of the cell. These light particles are essential for cell communication and support various biological processes by providing a form of non-chemical information transfer.
The Discovery and Scientific Basis of Biophotons
The discovery of biophotons is attributed to German physicist Fritz-Albert Popp in the 1970s. He found that biophotons are emitted by all living organisms and that these emissions are coherent – comparable to laser light. This coherence makes biophotons unique and distinguishes them from other forms of light. Popp’s research demonstrated that biophotons play a critical role in:
Information transfer within cells: Biophotons act as a communication network that increases the speed and precision of cellular processes.
Regulation of biological systems: They coordinate complex processes such as cell renewal, energy production, and adaptation to environmental factors.
Detection of stress in cell structures: Deviations in biophoton emission can indicate disruptions in biological systems.
The Role of Biophotons in Biological Systems
In biological systems, biophotons serve as a vital link in the communication between cell structures. These ultra-weak light signals:
Promote synchronization: Biophotons help align cellular processes, leading to more efficient functioning of biological systems.
Optimize energy flows: They contribute to the distribution and utilization of energy within cell structures.
Support adaptation: Biophoton emission dynamically changes in response to internal and external stimuli, enabling cells to better adapt.
Additionally, biophotons are involved in the regulation of oxidative processes and can modulate the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which is important for maintaining cell health.
How the Multiwave Oscillator Influences Biophoton Emission
The Multiwave Oscillator operates by emitting electromagnetic frequencies that resonate with the natural vibrations of cell structures. This process can:
Harmonize cell structures: The MWO’s frequencies help reduce disturbances in biological systems, leading to more efficient cellular functioning.
Enhance biophoton emission: By optimizing cell structures, the emission of biophotons can be amplified, improving communication and regulation within biological systems.
Support energy balance: The MWO can contribute to improved energy exchange within cell structures, which is essential for biophoton production.
The interaction between the MWO and biophoton emission suggests that electromagnetic frequencies can directly influence the coherence and intensity of the emitted light particles, further enhancing the overall efficiency of biological systems